Common doubts about the coronavirus! COVID-19, known as coronavirus 2019 or Coronavirus disease 2019, is an infection caused by a new type of coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, and is characterized by the appearance of flu-like symptoms, such as fever, headache and general discomfort, in addition to having difficulty breathing.
This infection initially arose in China, but was quickly spread by several countries, with COVID-19 now considered a pandemic. This rapid spread is mainly due to the easy transmission of the virus, which occurs through the inhalation of small droplets of saliva and respiratory secretions that contain the virus and remain suspended in the air.
For this reason, it is important that preventive measures are adopted to avoid contagion and transmission, helping to combat the pandemic. Learn more about the coronavirus, what are the symptoms, and how to identify them.
As it is a new virus, the information available is scarce and there are several doubts. Due to this, clarify some of the main doubts about COVID-19, below:
Common Doubts About The Coronavirus:
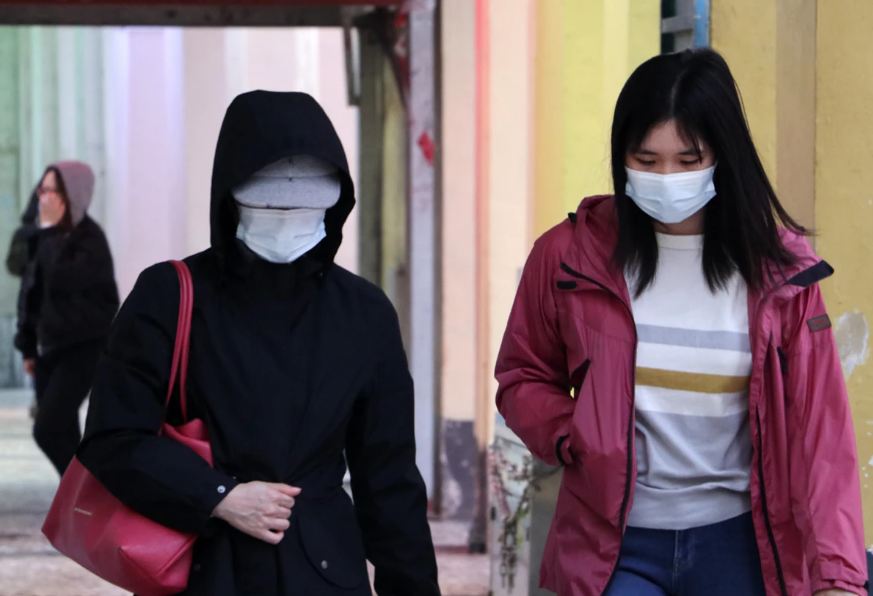
1. Is The Virus Transmitted Through The Air?
Transmission of COVID-19 occurs primarily through inhalation of small droplets of saliva or respiratory secretions that are present in the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or speaks, for example, or through contact with surfaces. contaminated.
For this reason, to avoid transmission, it is recommended that people who have been infected with the new coronavirus or who present symptoms indicating infection, wear protective masks.
There are no cases or evidence that the new coronavirus can be transmitted through mosquito bites, as is the case for other diseases such as dengue and yellow fever, for example, transmission is only considered to occur by inhalation of airborne drops containing the virus.
2. Can People Without Symptoms Transmit The Virus?
Yes, mainly due to the incubation period of the disease, that is, the period between infection and the appearance of the first symptoms, which in the case of COVID-19 are around 14 days.
In this way, the person can have the virus and not know it, being possible the transmission to other people.
For this reason, in the case of having no symptoms, but being included in the risk group or having had contact with people who were confirmed with the infection, it is recommended that a quarantine be carried out.
This because in this way it is possible to check if there was the development of symptoms and, if positive, to prevent the virus from spreading. Learn what quarantine is and how it should be done.
3. What is The Risk Group?
The risk group corresponds to the group of people who are more likely to develop more severe symptoms of the infection, mainly due to decreased activity of the immune system.
Thus, individuals in the risk group are older people, from the age of 60, and / or who have chronic diseases, such as diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD), kidney failure, or hypertension.
Likewise, the group of people who use immunosuppressants, those who are undergoing chemotherapy or those who recently underwent surgical procedures, including transplants, are also considered a risk group.
Although the most severe symptoms are more frequent in people who are in the risk groups, all people regardless of age or immune system are susceptible to infection.
For this reason, it is important to follow the recommendations of the health systems and the World Health Organization (WHO).
4. Do You Have a Vaccine?
Until now, there is no vaccine for the new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2 / COVID-19), and it is important that preventive measures are adopted to avoid contagion and transmission of the virus.
However, there are several investigations in development that aim to create a vaccine against this virus, which may be useful both for combat and for the prevention of the disease.
Existing vaccines, including influenza and pneumonia vaccines, do not provide protection against COVID-19, as they were developed based on the genetic sequence of the viruses responsible for these diseases, which are different from the genetic sequence of SARS-CoV2.
5. Do Antibiotics Treat Coronavirus?
Antibiotics have activity only against bacteria and certain fungi and parasites, having no effect on viruses. Likewise, when antibiotics are consumed without medical indication, this can promote microbial resistance to antibiotics
In addition, decrease the activity of the immune system, facilitating the emergence of other diseases.
Treatment for COVID-19 is carried out with support measures, such as hydration, rest and adequate nutrition, and should be performed in isolation to avoid transmission of the virus to other people.
So far, no antivirals have been identified that have action against the new type of coronavirus, however, studies have been carried out with the aim of determining drugs that have action against COVID-19.
6. Can I Travel?
It is important to consult the directions of the travel destination, this because certain countries will adopt measures to avoid the transmission of the virus, and there may be an indication of compulsory isolation when arriving at the place, for example.
In addition to that, some sites may indicate the closure of international airports, also aiming to prevent the spread of the virus.
Planes, trains, and buses typically do not have much air circulation and carry large numbers of people, which could also favor transmission. For this reason, in the event that the trip is necessary and authorized by the health organs.
It is important that precautionary measures are adopted, such as covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, avoiding touching the eyes and mouth with hands and wash your hands with soap and water frequently.
7. Can I Get Infected with The Coronavirus Through a Parcel?
According to the WHO, the probability of having contact with the virus through a package that came from a country with a large number of cases is very low, this because the package was possibly exposed to different conditions and variations in temperature and humidity, which could inactivate the virus.
Furthermore, it is not yet known exactly how long the new coronavirus is capable of remaining on surfaces.
A study carried out by scientists in the United States in March 2020 [1] , suggests that SARS-CoV-2 is able to continue being infectious on surfaces for days, mainly in plastic and stainless steel, with a shorter survival time. in the cardboard, which is normally the material where the parcels are sent.
For this reason, in the event that it is suspected that the package may be contaminated, although the probability is low, it can be disinfected with alcohol gel, in addition to washing hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling it.
8. Can Pets Transmit The Virus?
Transmission of COVID-19 from pets to humans has not yet been verified. So far, what is known is that transmission occurs through the inhalation of droplets of saliva and respiratory secretion that are suspended in the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes, for example.
Although the first cases of infection were from animals to people, the related animals are wild, therefore, they are not found frequently and, moreover, they were in inadequate conditions for consumption in terms of temperature and hygiene.
9. Does The Homemade Disinfectant Gel Work?
Although alcohol gel is widely used as a way to prevent infection with infectious agents, including viruses, homemade gel alcohol does not necessarily have the same efficacy. This is because, for it to work properly, it is important that you have the adequate concentration of alcohol capable of eliminating the infectious agent.
In addition, some recipes for homemade alcohol gel indicate the use of certain substances that can promote the development of microorganisms.
Therefore, to protect yourself, it is important to use a disinfectant gel containing 70% alcohol, both for hand hygiene and to disinfect surfaces and objects, and wash your hands with soap and water regularly.
Also, hand dryers or ultraviolet (UV) lights do not have a proven virus inhibiting or eliminating effect and therefore should not be used as a method of preventing COVID-19.
10. Do Higher Temperatures Inhibit Viruses?
So far, there is no information indicating the most suitable temperature to prevent the spread and development of the virus. However, the new coronavirus has already been identified in several countries with different climates and temperatures, indicating that the virus may not experience interference from these factors.
Likewise, the body temperature is between 36 and 37 ºC, regardless of the temperature of the water with which you take a bath or the temperature of the environment in which you live; thus, as the coronavirus is related to a series of symptoms, it is a sign that it manages to develop naturally in the human body, which has higher temperatures.
Diseases caused by viruses, such as flu and colds, occur more frequently during winter, since people tend to spend more time in closed places with little air circulation and with many people, which facilitates the transmission of the virus among the population.
However, since COVID-19 has already been identified in countries where it is summer, it is believed that the emergence of this virus is not related to the highest temperature in the environment, and can also be easily transmitted to people.
11. Does Vitamin-C Help to Protect Against Coronavirus (COVID-19)?
There is no scientific evidence to suggest that vitamin C helps fight the new coronavirus. What is known is that this vitamin helps improve the immune system, since it is rich in antioxidants that fight free radicals, prevent the appearance of infectious diseases and can alleviate the symptoms of the common cold.
Because it is rich in antioxidants, researchers in China are developing a study that aims to verify whether the use of vitamin C in critically ill patients can improve lung function, promoting an improvement in the symptoms of infection. , since this vitamin is capable of preventing the flu due to its anti-inflammatory action.
However, there is still no scientific evidence to confirm the effect of vitamin C on COVID-19, and when this vitamin is consumed in excess, there is an increased risk of developing kidney stones and changes at the gastrointestinal level.
To protect against the coronavirus, in addition to having a diet that improves the activity of the immune system, giving preference to foods rich in omega-3, selenium, zinc, vitamins and probiotics, such as fish, nuts, oranges, sunflower seeds, yogurt, tomato and watermelon, for example.
Despite the fact that garlic has antimicrobial properties, it has not yet been verified if it has any effect on the new coronavirus and therefore it is important to maintain a balanced diet.
It is also important to wash your hands well with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, avoid crowded and closed environments, and cover your mouth and nose whenever you need to cough or sneeze. In this way, it is possible to avoid contagion and transmission of the virus to other people.
12. Does Ibuprofen Worsen COVID-19 Symptoms?
A study carried out by scientists from Switzerland and Greece in March 2020, indicated that the use of ibuprofen was able to increase the expression of an enzyme that can be found in the cells of the lungs, kidneys and heart, which would make more severe respiratory symptoms.
However, this relationship was made based on only a study carried out in diabetics and taking into account the expression of the same enzyme, but present in cardiac tissue.
For this reason, it cannot be stated that the use of ibuprofen is related to the worsening of the signs and symptoms of COVID-19.
13. Does The Virus Survive For How Long?
An investigation carried out in March 2020 by American scientists indicated that the survival time of SARS-CoV-2, responsible for COVID-19, varies according to the type of surface it is on and the conditions of the environment. Therefore, in general, the virus can survive and remain infectious around:
*3 days for plastic and stainless steel surfaces;
*4 hours in the case of copper surfaces;
*24 hours in the case of cardboard surfaces;
*3 hours in the form of aerosols or in the air, which can be spread when an infected person is sprayed, for example.
Although it can be present on surfaces in its infectious form for a few hours, this type of contagion has not yet been determined.
However, it is recommended to disinfect surfaces that may contain the virus, in addition to using gel alcohol and washing your hands with soap and water regularly.
14. How Long Does it Take to Have The Test Result?
The time between the collection of the sample and the publication of the result may vary depending on the type of examination to be performed, and may take between 15 minutes and 7 days.
Results that are obtained in less time are those that are performed using rapid tests, such as immunofluorescence and immunochromatography tests.
The difference between these two is the sample collected: while immunofluorescence uses a sample from the airways, which is collected through a swab with a sample of nasal secretions, immunochromatography is performed from a small sample of blood.
In both tests, the sample comes into contact with the reagent and, if the person has the virus, the case of COVID-19 is confirmed.
Wrap-Up!
The test that takes the longest to obtain its results is PCR, which is a more specific molecular test, considered the gold standard, and which is mainly performed to confirm the positive case.
This test is performed from a blood sample or a sample collected from nasal or oral secretions, and indicates whether there is SARS-CoV-2 infection and the number of copies of the virus in the body, indicating how severe the disease.
















[…] last thing we would want is a second wave of the virus as that would send us back home. We may find out that we are better off working from home than the […]